Botuline Toxine
Botulinum toxin, type A also better known under the brand name Botox, has been used for years for cosmetic applications such as against wrinkles and excessive sweating.
Wrinkle treatment
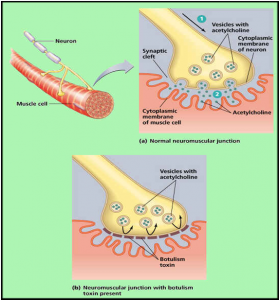
Botulinum toxin A is a protein that is able to temporarily relax the functioning of certain unwanted “muscles”. This protein is dissolved in a liquid called ‘physiological salt’ and injected directly into the relevant muscles. Botulinum toxin A locally blocks the transmission of these stimuli in the muscle (image b) and thereby reduces the excessive tension of the muscle. This allows wrinkles, folds and lines to be tightened and smoothed. Over time, the body recovers from the blocked nerve connection, which means that Botulinum toxin A must be applied regularly.
Treatment for excessive sweating
In the treatment of excessive sweating, botulinum toxin A inhibits the nerves that stimulate the sweat glands. The result is that the sweat glands no longer produce sweat, resulting in drier skin. In this way, people can get rid of their sweaty armpits, sweaty head and sweaty hands.
Other applications of Botulinum Toxin
The treatments with Botulinum toxin go a step further than just wrinkles and excessive sweating. What few people know is that there are indications that Botulinum toxin is also effective in the treatment of problems such as acne, rosacea, hypertrophic / keloid scars. The treatment can be applied to both young people from the age of 18 and older adults. Regular Botox treatments can prevent wrinkles, especially in ‘young people’, and in the elderly, the ‘often’ used deep wrinkles become more superficial after Botox treatments.
Sources
1: Xiao Z, Zhang M, Liu Y, Ren L. Botulinum toxin type a inhibits connective tissue growth factor expression in fibroblasts derived from hypertrophic scar. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2011 Oct;35(5):802-7. 2: Ziade M, Domergue S, Batifol D, Jreige R, Sebbane M, Goudot P, Yachouh J. Use of botulinum toxin type A to improve treatment of facial wounds: a prospective randomised study. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013 Feb;66(2):209-14. 3: Uyesugi B, Lippincott B, Dave S. Treatment of a painful keloid with botulinum toxin type A. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2010 Feb;89(2):153-5. 4: Xiao Z, Zhang F, Lin W, Zhang M, Liu Y. Effect of botulinum toxin type A ontransforming growth factor beta1 in fibroblasts derived from hypertrophic scar: a preliminary report. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2010 Aug;34(4):424-7.
